Introduction
Understanding the equipment requirements for ships under the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is crucial for ensuring maritime safety. The carriage requirements for GMDSS ships are determined by the areas in which they operate, as defined by the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS). This comprehensive guide will outline the necessary equipment for ships operating in different GMDSS Sea Areas, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and enhancing search and rescue capabilities.
GMDSS Sea Areas
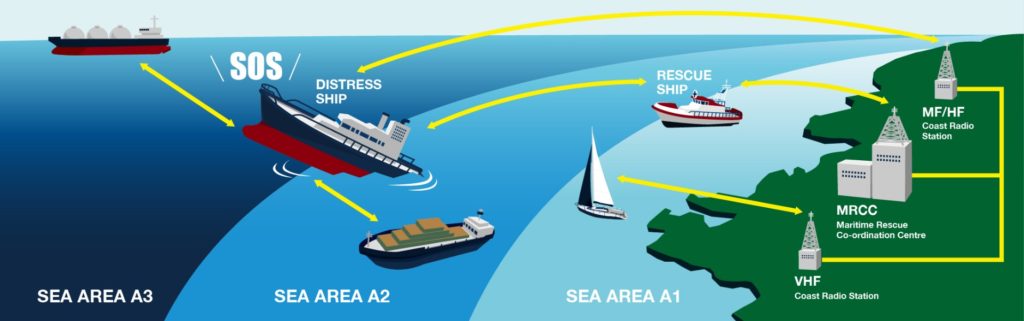
The GMDSS Sea Areas categorize the maritime zones based on their distance from shore and available communication coverage. Ships operating in these areas are required to carry specific communication and distress alerting equipment to facilitate effective maritime communication and ensure swift response in emergency situations.
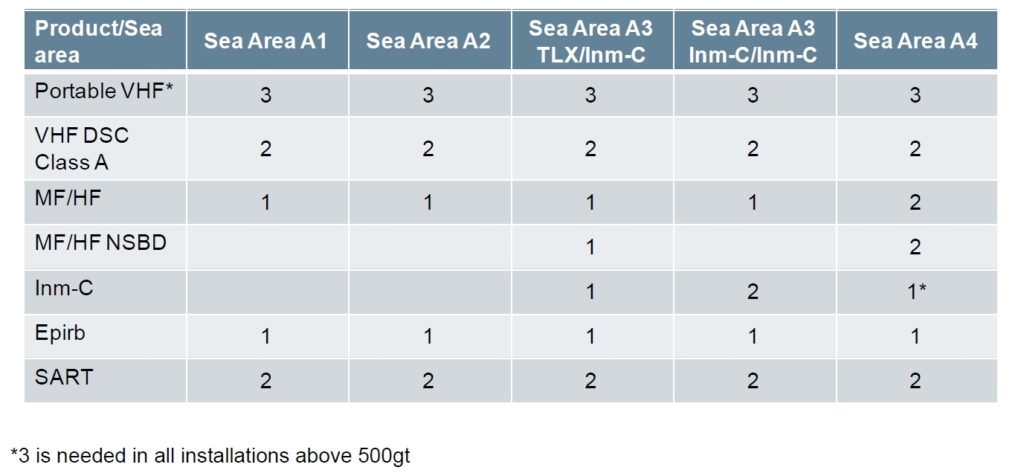
Minimum Requirements
Every GMDSS ship, as per SOLAS Chapter IV, regulation 7, must carry the following minimum equipment:
- A VHF radio installation capable of transmitting Digital Selective Calling (DSC) on channel 70, and radiotelephony on channels 16, 13, and 6.
- A Search and Rescue Transponder (SART), with two required on vessels over 500 Gross Registered Tonnage (GRT) and one on vessels between 300 and 500 GRT.
- A NAVTEX receiver for voyages in areas where NAVTEX service is provided.
- An Inmarsat Enhanced Group Call (EGC) receiver for voyages in areas without MSI services provided by NAVTEX or HF NBDP.
- A 406 MHz Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB), with the option for vessels trading exclusively in Sea Area A1 to fit a VHF DSC EPIRB.
Passenger Ships
In addition to the minimum requirements, passenger ships are mandated to have means of two-way on-scene radiocommunications using aeronautical frequencies for search and rescue purposes.
Equipment Carriage Requirements for GMDSS Sea Areas
The equipment carriage requirements vary based on the GMDSS Sea Areas, each offering specific guidelines for ensuring effective maritime communication and distress alerting capabilities. Let’s delve into the requirements for each area:
1. Radio Equipment – Sea Area A1
Ships exclusively operating in Sea Area A1 must fulfill the following requirements for ship-shore Distress Alerts transmission:
- Installation of a 406 MHz EPIRB or VHF DSC EPIRB.
- Alternatively, a MF DSC System or HF DSC System, or an Inmarsat ship earth station.
2. Radio Equipment – Sea Areas A1 And A2
Ships voyaging beyond Sea Area A1 but within Sea Area A2 must have:
- An MF radio installation for distress and safety purposes.
- A DSC watchkeeping receiver operating on designated frequencies.
- Means for initiating ship-to-shore Distress Alerts through specified equipment.
3. Radio Equipment – Sea Areas A1, A2 And A3
For voyages beyond Sea Areas A1 and A2 but within Sea Area A3, ships have two options to meet GMDSS requirements:
Option 1: Installation of an Inmarsat-C ship earth station, an MF radio installation, and means for initiating Distress Alerts. Option 2: Installation of an MF/HF radio installation with expanded capabilities and means for initiating Distress Alerts.
4. Radio Equipment – Sea Areas A1, A2, A3 And A4
For voyages in all Sea Areas, ships must be equipped with:
- An MF/HF radio installation capable of transmitting and receiving distress and safety communications.
- An MF/HF DSC watchkeeping receiver.
- Means for initiating ship-to-shore Distress Alerts.
Ensuring compliance with GMDSS equipment carriage requirements is paramount for SOLAS ships to enhance safety at sea. By adhering to these regulations and deploying the necessary communication and distress alerting equipment, ships can mitigate risks and facilitate effective response in emergency situations. For detailed guidelines on implementing GMDSS installations, reference should be made to IMO Circular COMSAR.1/Circ.32.





![Onwa KM-8A (BUNDLE) 8-inch Color TFT LCD GPS Chart Plotter with Class B+ AIS Transponder MFD [BUNDLE]](https://seanav.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/22-247x296.png)
Pingback: GMDSS Equipment programming Service during vessel flag or Vessel Name change