Best Practices for Testing GMDSS Equipment on Board Ships
At Seanav Marine, we understand the critical importance of ensuring the proper functioning of GMDSS (Global Maritime Distress and Safety System) equipment on board ships. Regular testing of this equipment is crucial to maintaining a safe and reliable communication system, which plays a vital role in maritime operations. In this article, we will outline the recommended frequency for testing GMDSS equipment and provide comprehensive insights into the testing procedures involved.
The Importance of Testing GMDSS Equipment
The GMDSS serves as a global communication network that enables ships to communicate distress signals, exchange safety-related information, and ensure effective search and rescue operations. As such, it is essential that all GMDSS equipment on board ships undergoes regular testing to guarantee its proper functioning in times of emergency.
Determining the Testing Frequency
When it comes to testing GMDSS equipment, the testing frequency depends on several factors, including regulatory requirements, the type of equipment installed, and the vessel’s operating area. While we acknowledge that regulations may differ across jurisdictions, we recommend adhering to the following guidelines for comprehensive testing:
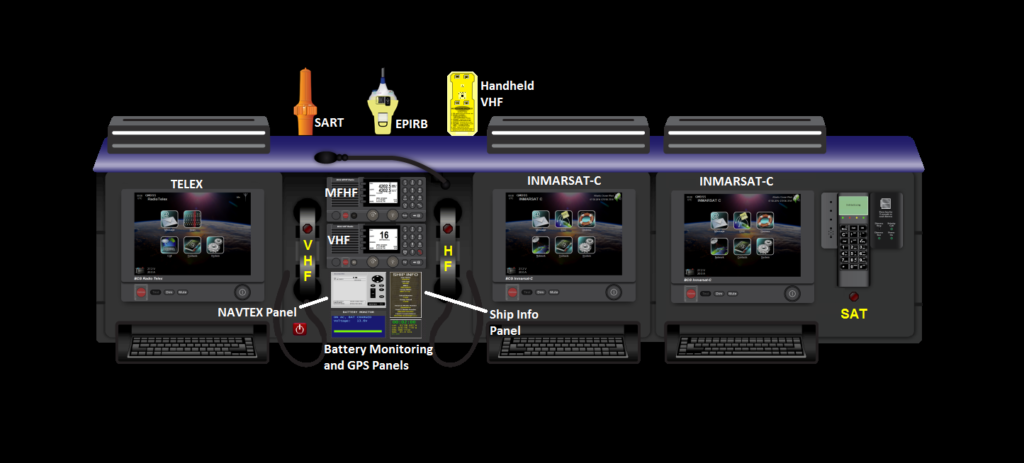
Daily Testing
Certain GMDSS equipment components should be tested on a daily basis to ensure their readiness for immediate use. These daily tests help identify any potential issues that may have arisen since the last test and allow for timely rectification. The components that should undergo daily testing include:
- Power Supply: Verify that the power supply to the GMDSS equipment is functioning correctly, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB): Conduct a daily functional self-test of the EPIRB, checking for proper battery voltage, antenna connection, and the absence of any fault indications.
- Search and Rescue Transponder (SART): Perform a daily functional self-test of the SART, confirming its operational readiness and ensuring it transmits an appropriate response when interrogated.
Weekly Testing
In addition to the daily tests, certain GMDSS equipment should undergo weekly testing to ensure its reliability and performance. These tests involve a more comprehensive evaluation of the equipment and include the following components:
- VHF Radio Equipment: Test the VHF radio system, including both the transmitter and receiver, to verify their operational effectiveness. Check the audio quality, antenna connection, channel selection, and overall performance.
- Navtex Receiver: Validate the proper functioning of the Navtex receiver, ensuring it receives and displays maritime safety information effectively.
Monthly Testing
On a monthly basis, further testing should be carried out to assess the overall functionality and performance of the GMDSS equipment. The monthly testing regime includes the following:
- MF/HF Radio Equipment: Conduct a detailed test of the MF/HF radio system, verifying its transmission and reception capabilities across various frequencies and assessing the audio quality.
- Inmarsat-C and SSAS (Ship Security Alert System): Perform a comprehensive test of the Inmarsat-C and SSAS systems, ensuring their proper operation, message transmission, and reception.
- Battery Performance: Evaluate the condition and capacity of the GMDSS equipment’s batteries, confirming their ability to provide sufficient power during emergencies.
Testing Procedures
It is important to follow standardized testing procedures to ensure consistency and accuracy across all testing activities. The following steps should be taken during each testing phase:
- Preparation: Gather all necessary testing tools and equipment, including reference manuals, testing forms, and any required software.
- Isolation of Equipment: Isolate the specific equipment being tested from the rest of the system to prevent interference and accurately evaluate its performance.
- Test Execution: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and regulatory guidelines to conduct the tests for each component of the GMDSS equipment. This may involve simulating distress signals, checking signal strengths, verifying transmission and reception capabilities, and assessing audio quality, among other parameters.
- Documentation: Thoroughly document the test results, including any abnormalities or issues encountered during the testing process. This information will be valuable for future reference and analysis.
- Maintenance and Repairs: If any faults or deficiencies are identified during the testing, promptly address them through appropriate maintenance or repair procedures. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of the GMDSS equipment.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
It is imperative to comply with the relevant regulatory standards and guidelines when conducting GMDSS equipment testing. Different regulatory bodies may have specific requirements, and it is essential to stay informed about any updates or changes in regulations that may affect the testing procedures. By adhering to these standards, you ensure the safety of the vessel, crew, and the effectiveness of the GMDSS system.
Importance of Professional Expertise
While regular testing of GMDSS equipment is crucial, it is equally important to engage the expertise of qualified professionals. Experienced marine technicians and radio surveyors possess the necessary knowledge and skills to conduct thorough testing, interpret results accurately, and address any issues effectively. Their expertise ensures that the GMDSS equipment operates optimally and complies with all applicable regulations.
Conclusion
Maintaining the reliability and effectiveness of GMDSS equipment on board ships is of utmost importance for maritime safety. Regular testing, conducted in accordance with recommended frequencies and standardized procedures, plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning of the equipment during emergency situations. By following the daily, weekly, and monthly testing guidelines outlined in this article, you can enhance the safety and communication capabilities of your vessel, contributing to a safer maritime environment for all.


Latest Products
YDK Technologies MKN020 Gyro compass connection box
AED 3,960.0Original price was: AED 3,960.0.AED 2,850.0Current price is: AED 2,850.0.Onwa KM-8X 5-in-1 Marine Bundle Set Radome – GPS, Chartplotter, EchoSounder, AIS, Radar
8-inch GPS Chart Plotter with AIS and Radar
Onwa KM-8A (BUNDLE) 8-inch Color TFT LCD GPS Chart Plotter with Class B+ AIS Transponder MFD [BUNDLE]