The Long-Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT) system is designed to globally identify and track ships, with the aim of enhancing shipping security, safety, and marine environment protection. The obligations for ships to transmit LRIT information and the rights and responsibilities of SOLAS Contracting Governments and search and rescue services are defined in regulation V/19-1 of the 1974 SOLAS Convention.
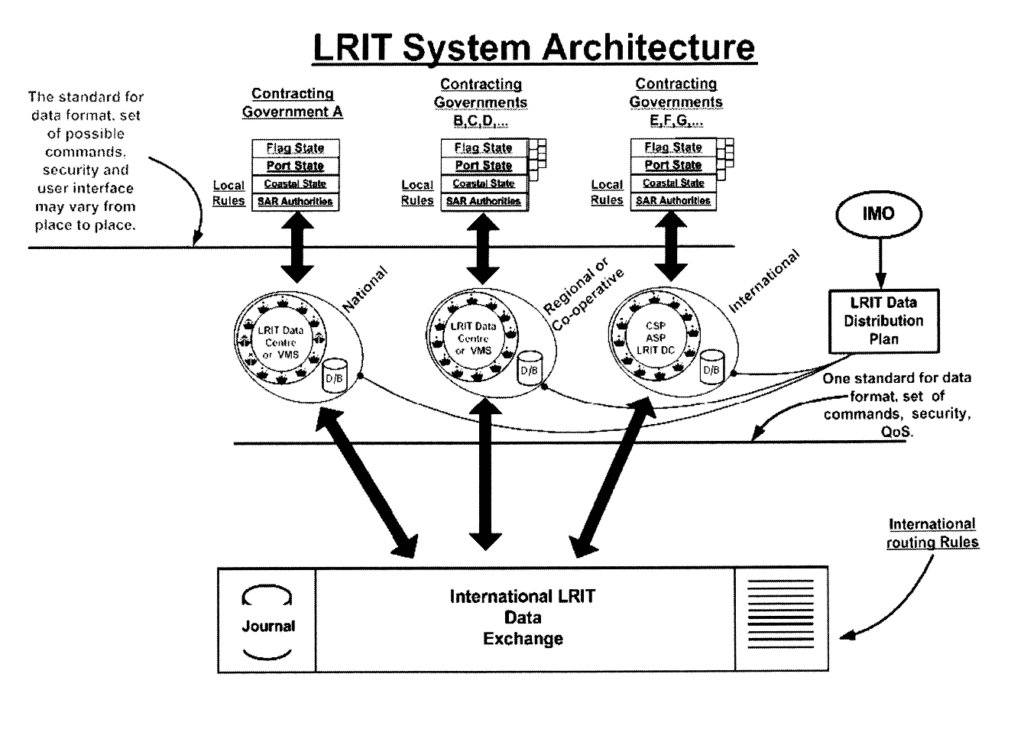
The LRIT system consists of several components:
- Shipborne LRIT information transmitting equipment: This equipment is installed on ships and transmits LRIT information, including the ship’s GNSS position, time, and equipment identification, based on the WGS 84 datum. The shipborne equipment automatically transmits this information at 6-hour intervals to the LRIT Data Centre designated by the ship’s flag Administration.
- Communication Service Provider(s) (CPS): The CPS establishes the communication path for transmitting LRIT information from the ship to the LRIT Data Centre. It ensures reliable communication between the ship and the LRIT system.
- Application Service Provider(s) (ASP): The ASP receives the LRIT information from the ship through the CPS, adds additional information to the message, and passes it to the associated LRIT Data Centre.
- LRIT Data Centre(s) (DC) and Vessel Monitoring System(s) (VMS): The LRIT Data Centre receives LRIT information from ships, stores it, and distributes it to authorized LRIT Data Users according to the LRIT Data Distribution Plan (DDP). The DC may also include Vessel Monitoring Systems for monitoring ship activities.
- LRIT Data Distribution Plan (DDP): The DDP contains the necessary information for the LRIT Data Centres to determine how LRIT information is distributed to the respective Contracting Governments.
- International LRIT Data Exchange (IDE): The IDE processes LRIT messages between LRIT Data Centres and routes them to the appropriate Data Centre based on the message’s address. It does not process or store the information within the LRIT messages.
LRIT information is provided to Contracting Governments and search and rescue services upon request through a system of National, Regional, and Cooperative LRIT Data Centres using the International LRIT Data Exchange. Each Administration (country) must provide the selected LRIT Data Centre with a list of ships entitled to fly its flag, which are required to transmit LRIT information. Administrations must promptly update these lists when changes occur.
The LRIT Coordinator plays a role in establishing LRIT system components, such as the IDE and IDC (International Data Centre). The LRIT Coordinator also performs administrative functions and reviews and audits certain aspects of the LRIT system’s performance on behalf of SOLAS Contracting Governments.
LRIT Data Users, such as flag States, port States, coastal States, or search and rescue services, may be entitled to receive or request LRIT information in accordance with regulation V/19-1 of the 1974 SOLAS Convention.


Latest Products
Onwa KM-8X 5-in-1 Marine Bundle Set Radome – GPS, Chartplotter, EchoSounder, AIS, Radar
8-inch GPS Chart Plotter with AIS and Radar
Onwa KM-8A (BUNDLE) 8-inch Color TFT LCD GPS Chart Plotter with Class B+ AIS Transponder MFD [BUNDLE]
Onwa KM-8C 8-inch Color TFT LCD GPS Chart Plotter with EchoSounder MFD